Blog
PIB
Daily PIB
Daily PIB/ 25 March
General Studies- III
Topic– Achievements of Indians in Science & Technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
BY Chrome Ias
Share
Trending
Latest Courses
Polar Science and Cryosphere (PACER) scheme
Context:
The Polar Science and Cryosphere (PACER) scheme has been approved for continuation during 2021-2026.
The PACER scheme:
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER) scheme comprising the Antarctic program, Indian Arctic program, Southern Ocean program and Cryosphere and Climate program.
- It is being implemented successfully through National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
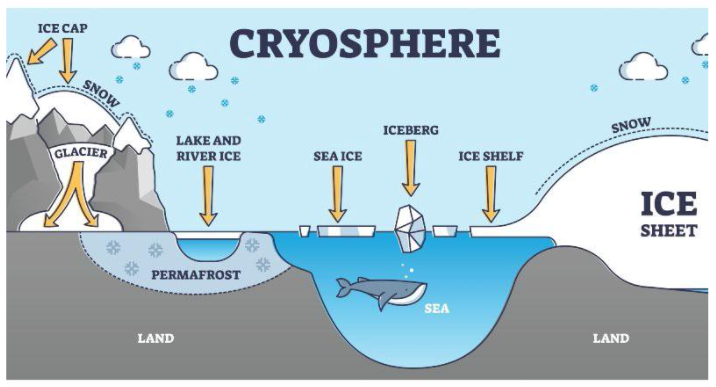
What is the cryosphere?
The cryosphere is the frozen water part of the Earth system.
- There are places on Earth that are so cold that water is frozen solid. These areas of snow or ice, which are subject to temperatures below 0°C 32°F for at least part of the year, compose the cryosphere.
- The term “cryosphere” comes from the Greek word, “krios,” which means cold.
Ice and snow on land are one part of the cryosphere.
- This includes the largest parts of the cryosphere, the continental ice sheets found in Greenland and Antarctica, as well as ice caps, glaciers, and areas of snow and permafrost.
- When continental ice flows out from land and to the sea surface, we get shelf ice.
The other part of the cryosphere is ice that is found in water.
This includes frozen parts of the ocean, such as waters surrounding Antarctica and the Arctic. It also includes frozen rivers and lakes, which mainly occur in polar areas.
Significance of Cryosphere:
- The components of the cryosphere play an important role in the Earth’s climate.
- Snow and ice reflect heat from the sun, helping to regulate our planet’s temperature.
- Because polar regions are some of the most sensitive to climate shifts, the cryosphere may be one of the first places where scientists are able to identify global changes in climate.
Polar Science and Cryosphere: Background
- Realizing the importance of Antarctica as a pedestal for scientific research, India launched the first of her Annual Scientific Expeditions to the Antarctica way back in 1981.
- This was followed by the country’s successful entry to the realms of Southern Ocean research in 2004 and the Arctic, three years later.
- To cater to the requirements of the Indian scientists in both the polar regions, two stations (Maitri and Himadri) have been established to serve as living-cum-research bases in the Antarctic and Arctic respectively.
- The focus areas of scientific studies in the Arctic and the Antarctic have been largely confined to earth, atmospheric and biological sciences.
- As regards the studies of the cryosphere, the research initiatives by Indian scientists in the Antarctic comprise monitoring of the glaciers in Dronning Maudland, studies of ice dynamics and energy balance and climatic reconstructions from ice core analyses.
- Considering the significance of the polar ice cap and the sea ice in the polar regions in modulating, it is proposed to initiate during the XII Plan period, a major national mission of cryospheric studies of both the polar regions as well as of the Himalaya.
PACER encompasses the following six components.
- Construction of polar research vessel
- Construction of the third research base in Antarctica
- Indian scientific endeavours in the Arctic
- Polar expeditions-Antarctica
- Replacement of Maitri station
- Southern Ocean
Objective of PACER scheme: To improve our understanding of Polar Science and cryosphere system.
Major achievements of the PACER scheme in the recent three years are:
- Executed 39th & 40th Indian Scientific Expedition to Antarctica.
- 41st Indian Scientific Expedition to Antarctica is ongoing.
- Clear-air atmospheric observatories containing automatic weather stations, a suite of sensors to measure aerosol and greenhouse gas concentrations has been established at Maitri and Bharati stations.
- Twenty-three research projects related to glaciology, marine science, polar biology, and atmospheric science were successfully carried out during 2019-20 Arctic Expedition.
- IndARC mooring system along with Hydrophone system was successfully retrieved and deployed in Kongsfjorden, Svalbard.
- Glaciological field campaigns were carried out in six benchmark glaciers in Chandra basin of Lahaul-Spiti region of Western Himalaya.
- Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) and Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) survey were conducted.
- Two new Automatic Weather Station (AWS) systems were installed at Baralacha La, a high elevation site in the arid Spiti region to strengthen infrastructure across the Chandra basin.
- The 11th Indian Southern Ocean Expedition was executed successfully.
- Sediment cores were collected from 13 locations and Argo floats were deployed to measure the different ocean parameters.
National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR):
- National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR) is India’s premier R&D institution responsible for the country’s research activities in the Polar and Southern Ocean realms.
- NCPOR is an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
General Studies- III
Topic– Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
National Aquifer Mapping and Management program (NAQUIM)
Context:
Out of nearly 33 lakh sq km geographical area of the country, a mappable area of around 25 lakh sq km has been identified by the CGWB to be covered under NAQUIM programme.
What is the NAQUIM programme?
National Aquifer Mapping and Management program (NAQUIM) was initiated in 2012 as a part of the ‘Ground Water Management and Regulation’ scheme with the objectives to delineate and characterize the aquifers and develop plans for sustainable ground water management in the country.
- The State-wise information is shared with States/Uts for implementation.
- It is implemented by Central Ground Water Board (CGWB).
Central Ground Water Board
Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) is the National Apex Agency entrusted with the responsibilities of providing scientific inputs for management, exploration, monitoring, assessment, augmentation and regulation of groundwater resources of the country.
- It works under the Ministry of Water Resources.
- It was established in 1970 by renaming the Exploratory Tubewells Organization under the Ministry of Agriculture.
- Later in 1972, it was merged with the Groundwater Wing of the Geological Survey of India during 1972.
General Studies- III
Topic– Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
Measures to Achieve Energy Transition towards Clean Energy
Context:
Government of India has set a target for installing 175 GW of Renewable Energy capacity (excluding large hydro) by the end of 2021-22.
It includes 100 GW from solar, 60 GW from wind, 10 GW from Biomass and 5 GW from Small Hydro.
Measures:
In order to become self-reliant in power generation and achieving energy transition towards clean energy, Government has inter-alia taken following measures:
- The renewable energy capacity to go up to 450 GW.
- Phase-wise retirement of old polluting coal based power plants.
- Setting up of Ultra Mega Renewable Energy Parks to provide land and transmission to RE developers on a plug and play basis.
- Schemes such as Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Surakshaevam Utthaan Mahabhiyan (PM-KUSUM), Solar Rooftop Phase II, 12000 MW CPSU Scheme Phase II, etc.
- Laying of new transmission lines and creating new sub-station capacity under the Green Energy Corridor Scheme for evacuation of renewable power.
- Notifying Bidding Guidelines for tariff based competitive bidding process for procurement of Power from Grid Connected Solar PV and Wind Projects.
- Declaring Large Hydro Power (LHPs) (>25 MW projects) as Renewable Energy source.
- Hydro Purchase Obligation (HPO) as a separate entity within Non-solar Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO).
- Tariff rationalization measures for bringing down hydro power tariff.
- Budgetary Support for Flood Moderation/Storage Hydro Electric Projects (HEPs).
Budgetary Support to Cost of Enabling Infrastructure, i.e. roads/bridges for hydro projects.
- ₹ 1.5 crore per MW for projects upto 200 MW
- ₹ 1.0 crore per MW for projects above 200 MW.
General Studies- II
Topic– Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Mission Karmayogi
“Mission Karmayogi”- National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB) has been carefully designed to lay the foundations for capacity building for Civil Servants.
- So that, they remain entrenched in Indian Culture and sensibilities and remain connected, with their roots, while they learn from the best institutions and practices across the world.
- The Programme will be delivered by setting up an Integrated Government Online Training-iGOT Karmayogi Platform.

Institutional framework for NPCSCB:
National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB) with the following institutional framework:-
- Prime Minister’s Public Human Resources (HR) Council,
- Capacity Building Commission.
- Special Purpose Vehicle for owning and operating the digital assets and the technological platform for online training,
- Coordination Unit headed by the Cabinet Secretary.
Salient Features:
- Supporting Transition from ‘Rules based’ to ‘Roles based’ HR Management. Aligning work allocation of civil servants by matching their competencies to the requirements of the post.
- To emphasize on ‘on-site learning’ to complement the ‘off-site’ learning,
- To calibrate all Civil Service positions to a Framework of Roles, Activities and Competencies (FRACs) approach and to create and deliver learning content relevant to the identified FRACs in every Government entity,
- To make available to all civil servants, an opportunity to continuously build and strengthen their Behavioral, Functional and Domain Competencies in their self-driven and mandated learning paths.
- To encourage and partner with the best-in-class learning content creators including public training institutions, universities, start-tips and individual experts,
- To undertake data analytics in respect of data emit provided by iGOT- Karmayogi.
Key Objective:
Mission Karmayogi aims to prepare the Indian Civil Servant for the future by making him more creative, constructive, imaginative, innovative, proactive, professional, progressive, energetic, enabling, transparent and technology-enabled. Empowered with specific role-competencies, the civil servant will be able to ensure efficient service delivery of the highest quality standards.
Public Human Resources Council:
- It will be comprising of select Union Ministers, Chief Ministers, eminent public HR practitioners, thinkers, global thought leaders and Public Service functionaries under the Chairmanship of Prime Minister.
- It will serve as the apex body for providing strategic direction to the task of Civil Services Reform and capacity building.
Capacity Building Commission (CBC):
A CBC is proposed to set up with a view to ensure a uniform approach in managing and regulating the capacity building ecosystem on collaborative and co-sharing basis.
The role of Commission will be as under-
- To assist the PM Public Human Resources Council in approving the Annual Capacity Building Plans.
- To exercise functional supervision over all Central Training Institutions dealing with civil services capacity building.
- To create shared learning resources, including internal and external faculty and resource centers.
- To coordinate and supervise the implementation of the Capacity Building Plans with the stakeholder Departments.
- To make recommendations on standardization of training and capacity building, pedagogy and methodology.
Significance:
- Capacity of Civil Services plays a vital role in rendering a wide variety of services, implementing welfare programs and performing core governance functions.
- A transformational change in Civil Service Capacity is proposed to be affected by organically linking the transformation of work culture, strengthening public institutions and adopting modern technology to build civil service capacity with the overall aim of ensuring efficient delivery of services to citizens.
iGOT-Karmayogi platform:
iGOT-Karmayogi platform brings the scale and state-of-the-art infrastructure to augment the capacities of over two crore officials in India.
- The platform is expected to evolve into a vibrant and world-class market place for content where carefully curated and vetted digital e-learning material will be made available.
- Besides capacity building, service matters like confirmation after probation period, deployment, work assignment and notification of vacancies etc. would eventually be integrated with the proposed competency framework.
Chrome facts for Prelims
Collaboration for Developing Atomic Energy
India is recognized globally as a nation with advanced nuclear technologies.
India has developed comprehensive capabilities in all stages of nuclear fuel cycle namely;
- mining,
- uranium production,
- fuel fabrication,
- nuclear power production,
- spent fuel reprocessing and
- waste management.
Inter-Governmental Agreement:
So far Inter Governmental Agreement (IGA) for co-operation in peaceful uses of nuclear energy have been signed with the following eighteen (18) countries:
Argentina, Australia, Bangladesh, Canada, Czech Republic, European Union, France, Japan, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, Namibia, Republic of Korea, Russia, Sri Lanka, United Kingdom, United States of America, Vietnam and Ghana.
Active Participation:
in the area of Nuclear Energy, currently India has active participation with:
- USA,
- France,
- Russia,
- Uzbekistan,
- Kazakhstan and
- Canada.
Key facts:
- Currently there is no collaboration with Israel on nuclear energy.
- The Government has accorded ‘in-principle’ approval of sites at Kovvada in Andhra Pradesh and ChhayaMithiVirdi in Gujarat for setting up nuclear power plants in cooperation with the United States of America.
Wings India 2022
Wings India 2022 is Asia’s largest event on Civil Aviation.
- Wings India, a biennial show, is organized by the Ministry of Civil Aviation of India (MoCA) and Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI) jointly.
- It is being organized at Begumpet Airport, Hyderabad.
- The theme of the event this year is ‘India@75: New Horizon for Aviation Industry’.
BY Chrome Ias
Trending
Latest Courses
For Daily Updates
Sign up for daily emails to get the latest Chrome IAS news.





