Blog
PIB
Daily PIB
Daily PIB/ 07 Feb
General Studies- III
Topic– Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc.
BY Chrome Ias
Share
Trending
Latest Courses
Cargo Ship sails from Patna to Pandu
Context:
An inland waterway vessel MV Lal Bahadur Shastri was flageed off from Patna to Guwahati.
This historic feat will usher a new era of growth for all the states of Northeast India.
Details:
- The vessel which started its journey from Patna is carrying 200 Metric Tonnes of foodgrains headed for Pandu in Guwahati & will travel via Bangladesh to reach the destination by early March, 2022.
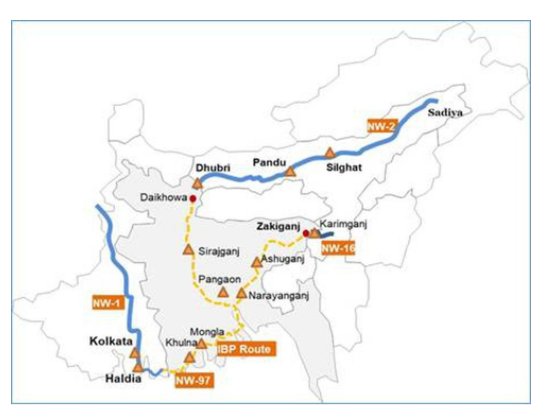
- The vessel starts its sail on National Waterway-1 (river Ganga) through Bhagalpur, Manihari, Sahibganj, Farakka, Tribeni, Kolkata, Haldia, Hemnagar; Indo Bangladesh Protocol (IBP) route through Khulna, Narayanganj, Sirajganj, Chilmari and National Waterway-2 through Dhubri, and Jogighopa covering a distance of 2,350 km.
- The vessel will take about 25 days to cover the entire voyage and is expected to reach Pandu in Guwahati by early March.
Waterway Usage Charges:
Ministry of Shipping has waived waterways usage charges to promote Inland water transport.
- The waterway usage charges has been waived initially for three years.
- This decision was taken to promote inland waterways as a supplementary, eco-friendly and cheaper mode of transport.
- Decision of waiving waterway charges will attract the industries to use the national waterways for their logistical needs.
Why this decision was taken?
- Water usage charge was applicable on use of all the national waterways by vessels.
- It was a hindrance in administration of traffic movement and collection of traffic data.
- Presently, Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) levies the waterway usage charges at a rate of Rs 0.02 per gross registered tonnage (GRT) per kilometer for plying of Inland cargo vessels.
- It levies Rs. 0.05 per gross registered tonnage (GRT) per kilometer for plying of Cruise vessels on national waterways.
Benefits:
- As the mode of transport is eco-friendly and cheaper, it will not only reduce the burden on other transport modes but also promote the ease of doing business.
- The decision is estimated to increase the inland waterway traffic movement to 110MMT in 2022-23 from 72MMTin 2019-20.
- It will benefit the economic activities and development in the region.
Significance:
- The waterways will cut through the landlocked access which has been crippling development in the region for long.
- The waterways not only remove this geographical hindrance on the road of progress in the region but also provides an economical, swift and convenient transportation for the businesses and people of the region.
National Waterways of India
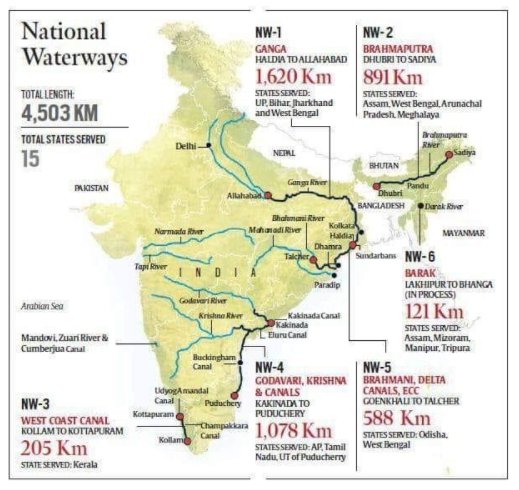
National Waterway 1:
- From Allahabad to Haldia with a distance of 1620 km.
- The NW1 run through the Ganges, Bhagirathi and Hooghly river system with having fixed terminals at Haldia, Farrakka and Patna.
- Floating terminals at the riverside cities like Kolkata, Bhagalpur, Varanasi and Allahabad.
- It is the longest National Waterway in India.
National Waterway 2:
- Brahmaputra River from Sadiya to Dhubri in Assam state.
- The NW2 is the third longest Waterway with a total length of 891 km.
National Waterway 3:
- The West Coast Canal or NW3 is in Kerala state and run from Kollam to Kottapuram.
- The 205 km long West Coast Canal is India’s first waterway with all-time navigation facility.
- The NW3 is consisting of West Coast Canal, Champakara Canal and Udyogmandal Canal.
- It runs through Kottappuram, Cherthala, Thrikkunnapuzha, Kollam and Alappuzha.
National Waterway 4:
- NW4 connect Kakinada to Pondicherry.
- The NW4 the second longest waterway of India
- Total length of 1095 km in Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
National Waterway 5:
- NW5 connects Odisha to West Bengal.
- It runs through the stretch on Brahmani River, East Coast Canal, Matai River and Mahanadi River.
- The 623 km long canal system handle the traffic of cargo such as coal, fertilizer, cement and iron.
National Waterway 6:
- NW6 is the proposed waterway in Assam.
- It will connect Lakhipur to Bhanga at River Barak.
- The 121 km long waterway will boost trade between Silchar (Assam) to Mizoram.
General Studies- II
Topic- Salient features of the Representation of People’s Act.
Registration of Political Parties
Context:
Former Punjab CM Amarinder Singh’s newly formed party Punjab Lok Congress has received its party symbol – Hockey stick and ball.

How are symbols allotted to political parties?
As per the guidelines, to get a symbol allotted:
- A party/candidate has to provide a list of three symbols from the EC’s free symbols list at the time of filing nomination papers.
- Among them, one symbol is allotted to the party/candidate on a first-come-first-serve basis.
- When a recognised political party splits, the Election Commission takes the decision on assigning the symbol.
Powers of Election Commission:
The Election Symbols (Reservation and Allotment) Order, 1968 empowers the EC to recognise political parties and allot symbols.
- Under Paragraph 15 of the Order, it can decide disputes among rival groups or sections of a recognised political party staking claim to its name and symbol.
- The EC is also the only authority to decide issues on a dispute or a merger. The Supreme Court upheld its validity in Sadiq Ali and another vs. ECI in 1971.
Types of symbols:
As per the Election Symbols (Reservation and Allotment) (Amendment) Order, 2017, party symbols are either:
- Reserved: Eight national parties and 64 state parties across the country have “reserved” symbols.
- Free: The Election Commission also has a pool of nearly 200 “free” symbols that are allotted to the thousands of unrecognised regional parties that pop up before elections.
Registration of political parties:
Registration of Political parties is governed by the provisions of Section 29A of the Representation of the People Act, 1951.
- A party seeking registration under the Section 29A of RP Act 1951 with the Election Commission has to submit an application to the Commission within a period of 30 days, following the date of its formation as per guidelines prescribed by the Election Commission of India in exercise of the powers conferred by Article 324 of the Commission of India and Section 29A of the Representation of the People Act, 1951.
- As per existing guidelines, the applicant party is, inter-alia, asked to publish proposed Name of party in two national daily newspapers and two local daily newspapers, on two days for submitting objections.
Political Parties in India
India has a multi-party system, where political parties are classified as national, state or regional level parties.
- The status of party is accorded by the Election Commission of India, and the same is reviewed occasionally.
- All parties are registered with the Election Commission.
- A special and unique election symbol is given to every registered party by the Election Commission.
Criterion for Recognition
The Election Commission has laid down certain criteria for a party to be recognised as national or state level parties.
National Party
A party has to live up to at least one of the following qualifications to be recognised as a national party:
- It has to win a minimum of two per cent of the seats in the Lok Sabha from at least three different states.
- In General Elections, the party must manage to win six per cent of the votes and win at least four Lok Sabha seats as well.
- The party is recognised as a ‘state level party’ in four or more states.
State Party
A party has to live up to at least one of the following qualifications to be acknowledged as a state party.
- The party has to win at least three seats or three per cent of the seats in the state legislative Assembly.
- It has to win minimum one seat in the Lok Sabha for every 25 seats or any fraction allotted to that concerned state.
- In a particular election, the party has to bag at least six per cent of the total votes, and also win one Lok Sabha and two Assembly seats.
- The status of a state party can still be bestowed upon an entity even if it fails to win any seats in the Lok Sabha or the Assembly, if it manages to win at least eight per cent of the total votes cast in the entire state.
Benefits of being a recognized party:
- If a party is recognised as a `National Party’ it is entitled for exclusive allotment of its reserved symbol to the candidates set up by it throughout India.
- If a party is recognised as a State Party, it is entitled for exclusive allotment of its reserved symbol to the candidates set up by it in the State in which it is so recognized.
- Recognised `State’ and `National’ parties need only one proposer for filing the nomination.
- They are entitled for two sets of electoral rolls free of cost at the time of revision of rolls and their candidates get one copy of electoral roll free of cost during General Elections.
- They also get broadcast/telecast facilities over Akashvani/Doordarshan during general elections.
- The travel expenses of star campaigners are not to be accounted for in the election expense accounts of candidates of their party.
General Studies- II
Topic- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Integrated Skill Development Scheme
Context:
Government is implementing various policy initiatives and schemes for supporting the development of textile sector.
About the ISDS:
- The Integrated Skill Development Scheme (ISDS) is introduced to cater to skilled manpower needs of Textile and related segments such as apparel, handicrafts, handlooms, jute, sericulture & technical textiles through skill development training programs.
- The Scheme will enhance the capacity and employability of the targeted trainees as it covers all facets of skill development such as basic training, skill upgradation, advanced training in emerging technologies, training of trainers, orientation towards modern technology, managerial skill etc.
Background:
The textiles sector has the second largest employment after agriculture sector and occupies an important position in the Indian economy.
- It also contributes 14% to industrial production, 4% to India’s GDP and constitutes to 13% of country’s export earning, with over 45 million people employed directly.
- As per the NSDC report, the overall employment in the textile and clothing sector expected to increase from about 33 to 35 million in 2008 to about 60 to 62 million by 2022.
- This would translate to an incremental humanresource requirement of about 25 million persons by 2022.
- Of this, the mainstream textile and clothing sector has the potential to employ about 17 million persons incrementally till 2022.
Scheme Reach
- The scheme has a wide spread reach with training being conducted in almost all Indian States/ UTs etc. Around 3,250 training centers are present across different Indian States, cities and rural areas including remote location, backwards region, left wing extremist affected area etc.
- Out of the total 664 districts Indian districts, around 357 districts have been covered under the scheme and trainees from different strata of the society are the major beneficiaries.
Chrome facts for Prelims
Statue of Equality
The PM dedicated to the nation the ‘Statue of Equality’ in Hyderabad, recently.
- The 216-feet tall Statue of Equality commemorates the 11th century Bhakti Saint Sri Ramanujacharya, who promoted the idea of equality in all aspects of living including faith, caste and creed.
- The Statue is made of ‘PANCHALOHA’, a combination of five metals: gold, silver, copper, brass and zinc.
- It is among one of the tallest metallic statues in sitting position in the world.
- It is mounted on a 54-feet high base building, named ‘Bhadra Vedi’.
- It has floors devoted for a Vedic digital library and a research Centre, ancient Indian texts, a theatre, an educational gallery detailing works of Sri Ramanujcharya.

BY Chrome Ias
Trending
Latest Courses
For Daily Updates
Sign up for daily emails to get the latest Chrome IAS news.





