Blog
PIB
Daily PIB
Daily PIB/ 05 Feb
General Studies- I
Topic- The Freedom Struggle – its various stages and important contributors/contributions from different parts of the country.
BY Chrome Ias
Share
Trending
Latest Courses
Chauri Chaura incident
Context:
Heroes of freedom struggle on completion of hundred years of Chauri Chaura incident on 4th February.
February 4 marks the beginning of the 100th year of the “Chauri Chaura” incident, a landmark in India’s freedom movement.
About the ‘Chauri Chaura’ incident:
- The “Chauri Chaura” incident took place on 4 February 1922 at Chauri Chaura in the Gorakhpur district of Uttar Pradesh.
- A large group of freedom fighters participating in the Non-cooperation movement, clashed with local police who opened fire.
- The locals attacked the police station and set fire to it, killing its occupants.
- Mahatma Gandhi, who was completely against violence, stopped the Non-cooperation movement on 12 February 1922.
How the British reacted?
After an immediate crackdown, the British colonial rulers arrested hundreds of people for the “Chauri Chaura” incident.
- Over 200 people were tried on charges of rioting; six of them died in police custody.
- The trial lasted eight months; most of those held were sentenced to death.
- The Allahabad High Court in April 1923 reviewed the death sentences; 19 were confirmed and 110 were given life sentence.
Effect on Non-Cooperation Movement:
- Mahatma Gandhi condemned the crime of the policemen’s killing.
- He disbanded the volunteer groups in nearby villages, and a Chauri Chaura Support Fund was set up to demonstrate “genuine sympathy” and seek atonement.
- Gandhi decided to stop the Non-Cooperation Movement, which he saw as having been tainted by unforgivable violence.
General Studies- I
Topic- Distribution of key natural resources across the world, including South Asia and the Indian sub-continent.
Lithium deposits in Mandya district of Karnataka
Context:
Preliminary survey shows deposits of Lithium in Mandya district of Karnataka.
The preliminary surveys on surface and limited subsurface by Atomic Minerals Directorate for Exploration and Research (AMD), have shown presence of Lithium resources of 1,600 tonnes (inferred category) in the pegmatites of Marlagalla – Allapatna area, Mandya district, Karnataka.
About Lithium:
- Lithium is part of the alkali metal group.
- Like all alkali metals it has a single balance electron that it readily gives up to form a cation or compound.
Characteristics and Properties:
- At room temperature lithium is a soft metal that is silvery-white in color.
- It is the least dense of the solid elements and is the lightest of all the metals.
- It has the highest specific heat capacity of any solid element.
- Lithium’s single balance electron allows it to be a good conductor of electricity. It is flammable and can even explode when exposed to air and water.
- It needs to be stored in mineral oil as it will react with air or water.
- It can cause burns if it comes into contact with the skin.
Uses:
- Lithium is a key element for new technologies and finds its use in ceramics, glass, telecommunication and aerospace industries.
- The well-known uses of Lithium are in Lithium ion batteries, lubricating grease, high energy additive to rocket propellants, optical modulators for mobile phones and as convertor to tritium used as a raw material for thermonuclear reactions i.e. fusion.
- The thermonuclear application makes Lithium as “Prescribed substance” under the Atomic Energy Act, 1962 which permits AMD for exploration of Lithium in various geological domains of the country.
- Due to the continuously increasing demand of Lithium ion batteries, the requirement of Lithium has increased over last few years.
Significance of findings:
- The significance and quantity of lithium resources in Marlagalla-Allapatna area, Mandya district, Karnataka may be established only after the completion of exploration in the entire area.
- Subsequently, plan for commercial exploitation of the lithium deposits can commence after the technical, social and economic feasibility studies in the area.
General Studies- II
Topic- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
National Innovations in Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA)
Context:
Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), Government of India has launched a flagship network project “National Innovations in Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA)”.
It aimed at strategic research on adaptation and mitigation, demonstration of technologies on farmers’ fields and creating awareness among farmers and other stakeholders.
Steps taken in the field of Climate Smart Agriculture:
- Developed climate resilient varieties for different abiotic and biotic stresses in major crops. So far 8 climate resilient varieties have been released in rice, green gram, maize and lentil;
- Developed and popularized 65 location-specific climate resilient/smart technologies for wider adoption among the farming communities;
- Prepared 650 district agricultural contingency plans and sensitized State officials for preparedness through 54 State-level interface meetings;
- Developed, evaluated and commercialized implements (raised bed planter-cum-herbicide applicator, maize harvester, zero till planter, etc.) for small farm mechanization suiting to dryland ecologies;
- Climate smart technologies developed involving farmers in risk assessment and adaptation techniques in 151 clusters covering 446 villages, with a footprint of 2,13,421 households, on 2,35,874 hectares of land;
- Capacity building programs have been taken up involving 5.15 lakhs comprising researchers, farmers, entrepreneurs, line department officials, policy makers and NGOs in the field of climate resilient agriculture.
Further, the climate smart agriculture is promoted under the Central Sector Schemes of Pradhan Mantri Krishi SinchayeeYojna (PMKSY), Parmparagat Krishi Vikas Yojna (PKVY), Soil Health Mission (SHM), National Bomboo Mission (NBM) and Sub Mission on Agro Forestry (SMAF).
National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA),
National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) has been formulated for enhancing agricultural productivity especially in rainfed areas focusing on integrated farming, water use efficiency, soil health management and synergizing resource conservation.
- NMSA is one of the eight Missions under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC).
- NAPCC has identified the focus areas on Dryland agriculture, risk management, access to information and use of biotechnology under NMSA.
Implementation strategies:
- Integrated farming system: under the Integrated Farming System activities like horticulture, livestock, fishery, agroforestry, value addition are to be taken up along with cropping system.
- Adopting Technology: NMSA seeks to achieve its objectives by popularising resource conservation technologies and introducing practices that will support mitigation efforts in times of extreme climatic events or disasters like prolonged dry spells, floods etc.
- Water resource management: To focus on effective management of available water resources and enhancing water use efficiency.
- Agronomic practices: NMSA envisage encouragement of improved agronomic practices for higher farm productivity like improved soil treatment, increased water holding capacity, judicious use of chemicals and enhanced soil carbon storage.
- Creating Database: Through creation of database on soil resources by land use survey, soil profile study and soil analysis on GIS (Geographic Information System) platform NMSA seek to facilitate adoption of location and soil-specific crop management practices & optimise fertiliser use.
- Integrated Nutrient Management Practices: For improving soil health, enhancing crop productivity and maintaining quality of land and water resources, NMSA will focus on promoting location and crop specific integrated nutrient management practices.
- Interventions: NMSA seeks to disseminate and adopt rainfed technologies with greater reach in disadvantaged areas. It is envisaged to be done by coordination, convergence and leveraging investments from other schemes like MGNREGS, National Food Security Mission, National Mission for Agricultural Extension & Technology etc.
Significance:
The Mission acknowledges that the risks to the Indian agriculture sector due to climatic variabilities and extreme events would be accentuated. On implementation it can help the agricultural sector and can help farmers mitigate the developing risks due to climate change.
General Studies- II
Topic- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Gobardhan scheme
Ministry of Jal shakti has launched the GOBAR (Galvanizing Organic Bio-Agro Resources) – DHAN scheme. The scheme is being implemented as part of the Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin).
Aim:
- The scheme aims to positively impact village cleanliness and generate wealth and energy from cattle and organic waste.
- The scheme also aims at creating new rural livelihood opportunities and enhancing income for farmers and other rural people.
Key features of the Scheme:
- The scheme focuses on managing and converting cattle dung and solid waste in farms to useful compost, biogas and bio-CNG.
- It will also help in keeping the village clean while increasing income of farmers and cattle herders.
- Under it, biogas generation will help to increase self-reliance in energy utilized for cooking and lighting.
- The villagers will be mobilized to create self-help groups (SHGs) and creative societies that will help in clean energy and green jobs initiative.
- Gram panchayats will play key role in implementation of this scheme under which bio-gas plants from cattle dung will be set up at individual or community level.
- The central and state governments will provide funds in the ratio of 60:40, which will depend upon the number of households in villages.
Significance:
- The scheme will be hugely beneficial for country as India is home to highest cattle population in world (around 300 million in number) which produces around 3 million tonnes of dung.
- It will encourage farmers to consider dung and other waste not just as waste but as source of income.
General Studies- III
Topic- Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nano-technology, bio-technology and issues relating to intellectual property rights.
Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems (CCTNS)
Context:
Use of Crime and Criminal Tracking Networks and Systems (CCTNS) and Inter-Operable Criminal Justice System (ICJS) is regularly reviewed by the Government with the States/ Union Territories.
What is the CCTNS Project?
- CCTNS (Crime and Criminal Tracking Network & Systems) is a Mission Mode Project under the National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) of Govt. of India.
- It was initiated in June 2009 which aims at creating a comprehensive and integrated system for enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of policing at the Police Station level.
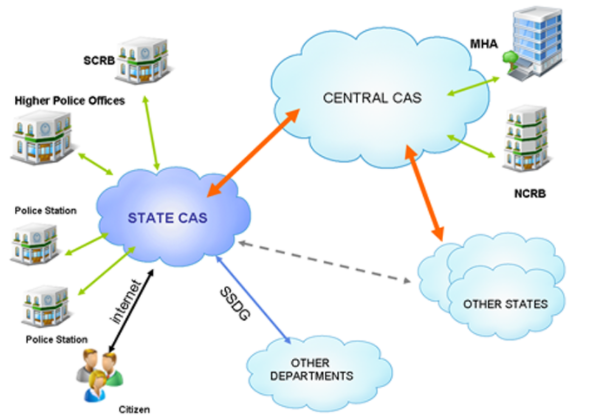
Objectives of ‘CCTNS’:
The objectives of the Scheme can broadly be listed as follows:
- Make the Police functioning citizen friendly and more transparent by automating the functioning of Police Stations.
- Improve delivery of citizen-centric services through effective usage of ICT.
- Improve Police functioning in various other areas such as Law and Order, Traffic Management etc.
- Facilitate Interaction and sharing of Information among Police Stations,
- Districts, State/UT headquarters and other Police Agencies.
- To improve overall efficiency and bring transparency through egovernance.
Benefits:
- The Full implementation of the Project with all the new components would lead to a Central citizen portal having linkages with State level citizen portals.
- It will provide a number of citizen friendly services like Police Verification for various purposes including passport verification, reporting a crime including cyber-crime and online tracking of the case progress etc.
- The project will enable National level crime analytics to be published at increased frequency.
- It will help the policy makers as well as lawmakers in taking appropriate and timely action.
BY Chrome Ias
Trending
Latest Courses
For Daily Updates
Sign up for daily emails to get the latest Chrome IAS news.





