General Studies- III
Topic– Achievements of Indians in Science & Technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
Drone use permission to a Telangana University
Context:
Drone use permission to Professor Jayashankar Telangana State Agricultural University (PJTSAU)
Highlights:
- The Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA) and the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) have granted conditional exemption to Professor Jayashankar Telangana State Agricultural University (PJTSAU) to use drones.
- The permission is aligning with the objectives of the Government of India to promote the scope of drone usage in the country.
- The drone usage exemption has been granted for the evaluation and standardization of plant protection solutions, Agri Spraying, and developing protocols for the diagnosis of major pests and diseases in PJTSAU research farms in Telangana.
Drone Regulations in India:
According to India’s national aviation authority, the Ministry of Civil Aviation, flying a drone is legal in India.
In 2018, country’s first Civil Aviation Requirements (CAR) for drones was announced by India’s Directorate General of Civil Aviation.
General Rules for Flying a Drone in India:
Based on our research and interpretation of the laws, here are the most important rules to know for flying a drone in India.
- All drones except those in the Nano category must be registered and issued a Unique Identification Number (UIN).
- A permit is required for commercial drone operations (except for those in the Nano category flown below 50 feet and those in the Micro category flown below 200 feet).
- Drone pilots must maintain a direct visual line of sight at all times while flying.
- Drones cannot be flown more than 400 feet vertically.
- Drones cannot be flown in areas specified as “No Fly Zones”, which include areas near airports, international borders, Vijay Chowk in Delhi, State Secretariat Complex in State Capitals, strategic locations, and military installations.
- Permission to fly in controlled airspace can be obtained by filing a flight plan and obtaining a unique Air Defense Clearance (ADC)/Flight Information Center (FIC) number.
- Foreigners currently are not allowed to fly drones in India. For commercial purpose they are required to lease the drone to an Indian entity that in turn supports to acquire UIN and UAOP from DGCA.
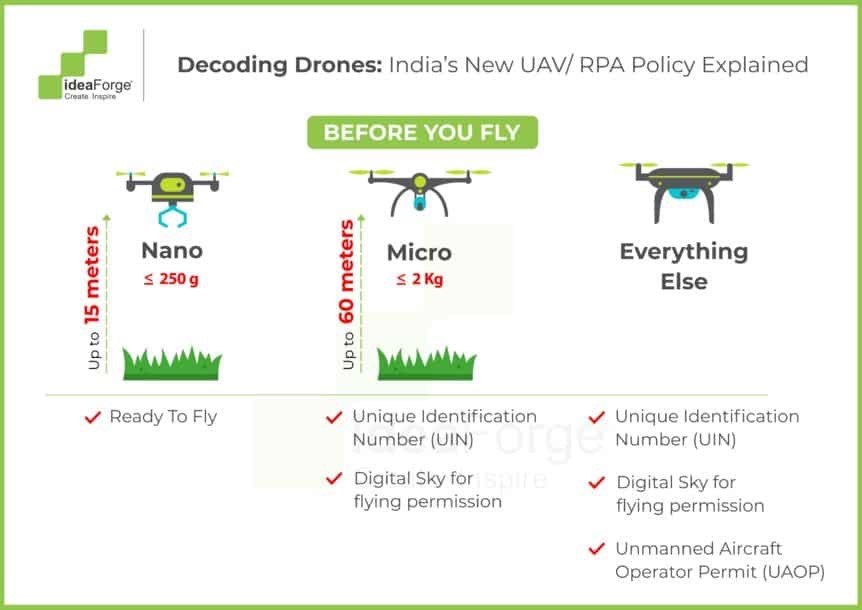
Drone Categories in India
Registration is required for all but the Nano category.
- Nano: Less than or equal to 250 grams
- Micro: From 250 grams to 2kg
- Small: From 2kg to 25kg
- Medium: From 25kg to 150kg
- Large: Greater than 150kg
Limitation on Drone flying:
- According to the new rules, drones will not be allowed to operate beyond visual line of sight or for delivery of goods.
- The use of these gadgets will be limited to surveys, photography, security and various information gathering purposes.
- The final rules come at a time when the pandemic has highlighted the role of technology in reducing human interface and costs.
Benefits of Drones:
- Use of drones in commercial, safety, law and order, disaster management and surveillance operations reduce manpower requirement and costs.
- Drones offer low-cost, safe and quick aerial surveys for data collection and are useful for industries such as power, mining, realty and oil and gas exploration.
General Studies- II
Topic– Statutory, regulatory and various quasi-judicial bodies.
National Startup Advisory Council (NSAC)
Context
Central Government notifies the structure of National Startup Advisory Council.
Highlights:
- The Central Government has notified the structure of the National Startup Advisory Council.
- It will advise the Government on measures needed to build a strong ecosystem for nurturing innovation and startups in the country.

Functions of NSAC
- The Council will suggest measures to foster a culture of innovation amongst citizens and students.
- Promote innovation in all sectors of economy across the country, including semi-urban and rural areas,
- Support creative and innovative ideas through incubation and research and development to transform them into valuable products,
- Processes or solutions to improve productivity and efficiency and create an environment of absorption of innovation in industry.
Structure of NSAC
- The National Startup Advisory Council will be chaired by Minster for Commerce & Industry.
- The Council will consist of the non-official members, to be nominated by Central Government.
- The nominees of the concerned Ministries/Departments/Organisations, not below the rank of Joint Secretary to the Government of India, will be ex-officio members of the Council.
- Joint Secretary, Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade will be the Convener of the Council
Term:
The term of the non-official members of the Startup Advisory Council will be for a period of two years.
Fundamentals
NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development)
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) is an Apex Development Financial Institution in India.
- The Bank has been entrusted with “matters concerning Policy Planning and Operations in the field of credit for Agriculture and other Economic activities in Rural areas in India”.
- NABARD is active in developing Financial Inclusion policy.
- It is one of the premier agencies providing developmental credit in rural areas.
- NABARD Head Office at Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
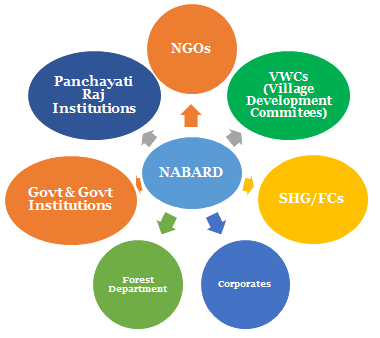
Background
NABARD was established on the recommendations of B.Sivaraman Committee, to implement the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development Act 1981.
- It replaced the Agricultural Credit Department (ACD) and Rural Planning and Credit Cell (RPCC) of Reserve Bank of India, and Agricultural Refinance and Development Corporation (ARDC).
- NABARD came into existence on 12 July 1982 by transferring the agricultural credit functions of RBI and refinance functions of the then Agricultural Refinance and Development Corporation (ARDC).
- NABARD is India’s specialised bank for Agriculture and Rural Development in India.
- International associates of NABARD include World Bank-affiliated organisations and global developmental agencies working in the field of agriculture and rural development.
- It was set up with an initial capital of Rs.100 crore, its’ paid up capital stood at Rs.10,580 crore as on 31 March 2018.
- Consequent to the revision in the composition of share capital between Government of India and RBI, NABARD today is fully owned by Government of India.
Vision:
Development Bank of the Nation for Fostering Rural Prosperity.
Mission:
Promote sustainable and equitable agriculture and rural development through participative financial and non-financial interventions, innovations, technology and institutional development for securing prosperity.
Chrome facts for Prelims
Good Friday
Good Friday is celebrated on Friday, April 2, 2021.
- Good Friday is observed on the Friday before Easter.
- It is the day on which Christians annually observe the commemoration of the Crucifixion of Jesus Christ.
- From the early days of Christianity, Good Friday was observed as a day of sorrow, penance, and fasting.
Army War College (AWC)
AWC celebrated its Golden Jubilee on 2 April, to mark 50 glorious years of its inception as the premier training institute of Indian Army.
- The Army War College, Mhow (A.W.C.) is a tactical training and research institution of the Indian Army located in Mhow, Madhya Pradesh.
- Since, its modest beginning in 1971, The College has evolved into a magnificent and vibrant cradle of learning and development of military leadership.
- The College is the fountain-head of all tactical training in the Indian Army and solely responsible for training officers of the Indian Armed Forces and from friendly foreign countries.





