Source: The Hindu, Live Mint and Indian Express
INDIA CUTS OFF UN PANEL AFTER JAMMU & KASHMIR REPORT
Context: Reacting angrily to a submission from the Geneva-based Human Rights Council (HRC) on the alleged violations in Jammu and Kashmir, India has informed the United Nations body that it will no longer entertain any communication with the HRC’s Special Rapporteurs on its report.
Essentials
United Nations Human Rights Council
- The Human Rights Council is an inter-governmental body within the United Nations system responsible for strengthening the promotion and protection of human rights around the globe and for addressing situations of human rights violations and make recommendations on them.
- It has the ability to discuss all thematic human rights issues and situations that require its attention throughout the year.
- The Human Rights Council was established in 2006 by a Resolution as a subsidiary body to the UN General Assembly.
- It replaced the former Commission on Human Rights, which operated from 1946 to 2006.
Membership of the Human Rights Council
- The Council is made of 47 Member States, which are elected by the majority of members of the General Assembly of the United Nations through direct and secret ballot.
- The General Assembly takes into account the candidate States’ contribution to the promotion and protection of human rights, as well as their voluntary pledges and commitments in this regard.
- The Council’s Membership is based on equitable geographical distribution. Seats are distributed as follows:
- African States: 13 seats
- Asia-Pacific States: 13 seats
- Latin American and Caribbean States: 8 seats
- Western European and other States: 7 seats
- Eastern European States: 6 seats
- Members of the Council serve for a period of three years and are not eligible for immediate re-election after serving two consecutive terms.
- At present India is not its member.
- Iceland was elected in July 2018 to serve as a member from 13 July 2018 to 31 December 2019 to replace the vacancy left by the United States following its decision to withdraw its membership.
Functions
- The Human Rights Council has created or renewed the mandates of various “special procedures.”
- The special procedures are experts appointed to monitor human rights around priority themes or in specific countries with serious human rights problems.
- The special procedures may be individual experts (“special rapporteurs” or “independent experts”) or working groups.
- The Council also manages the Universal Periodic Review, a process through which each UN Member State’s overall human rights record is reviewed.
Sessions
- The Council conducts its substantive work primarily in Regular Sessions and Special Sessions.
- Regular Sessions are held no fewer than three times a year, usually in March, June, and September.
Presidency and Bureau
- The Bureau of the Council consists of five people – one President and four Vice-presidents – representing the five regional groups.
- They serve for a year, in accordance with the Council’s annual cycle.
INDIA ADOPTS NEW STANDARDS FOR MEASURING UNITS KILOGRAM
Context: On May 20, 2018, the kilogram, the measurement of mass, joined other standard units of measure such as the second, metre, ampere, Kelvin, mole and candela that would no longer be defined by physical objects.

Essentials
- The measures are all now defined on the basis of unchanging universal, physics constants.
- The kilogram now hinges on the definition of the Planck Constant, a constant of nature that relates to how matter releases energy.
- Earlier, the kilogram derived its provenance from the weight of a block of a platinum-iridium alloy, called the Grand K, housed at the International Bureau of Weights and Measures in France.
- Recently, countries also unanimously approved updates to three other key units- the kelvin for temperature, the ampere for electrical current and the mole for the amount of a substance.
- The CSIR-National Physical Laboratory (NPL) is India’s official reference keeper of units of measurements.
How does the new system work?
- There is a quantity that relates weight to electrical current, called Planck’s constant – named after the German physicist Max Planck and denoted by the symbol h.
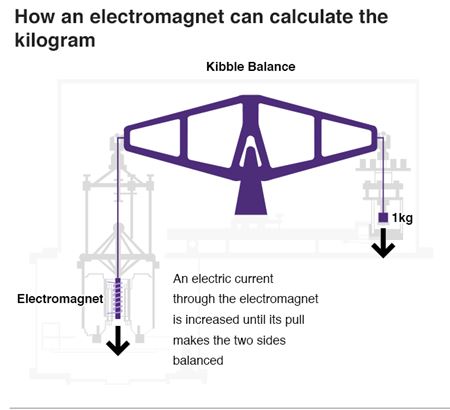
- But h is an incredibly small number and to measure it, the research scientist Dr Bryan Kibble built a super-accurate set of scales called Kibble balance.
- Kibble balance is an electromechanical weighing machine that can be used to measure the Planck Constant.
- The Kibble balance has an electromagnet that pulls down on one side of the scales and a weight – say, a kilogram – on the other.
- The electrical current going through the electromagnet is increased until the two sides are perfectly balanced.
- By measuring the current running through the electromagnet to incredible precision, the researchers are able to calculate h to an accuracy of 0.000001%.
- So, in principle, scientists can define a kilogram, or any other weight, in terms of the amount of electricity needed to counteract the weight (gravitational force acting on a mass).
- This breakthrough has paved the way for Le Grand K to be deposed by “die kleine h”.
Why kill off the kilogram?
- The Grand K has been at the forefront of the international system of measuring weights since 1889. Several close replicas were made and distributed around the globe.
- But the master kilogram and its copies were seen to change – ever so slightly – as they deteriorated.
- The new formula-based definition of the kilogramme will have multiple advantages over the precision-crafted metal lump that has set the standard for more than a century.
- Unlike a physical object, the formula cannot pick up particles of dust, decay with time or be dropped and damaged. It also is expected to be more accurate when measuring very, very small or very, very large masses.
- The updated definition will, in time, spare nations the need to occasionally send their kilos back to France for calibration against the Grand K. The new system will allow anyone with a Kibble balance to check their weights anytime and anywhere.
- In a world where accurate measurement is now critical in many areas, such as in drug development, nanotechnology and precision engineering – those responsible for maintaining the international system had no option but to move beyond the Grand K to a more robust definition.
Effects
- An updated kilogram doesn’t mean that weights everywhere will be thrown off balance. For everyday measurements, consumers wanting to calibrate their instruments — whether it’s for high-precision drug manufacturing or retail weighing machines — will continue doing it the same way.
A mini revolution
- But scientists are hailing the vote as a mini revolution in the field of weights and measures. One of the things this (new) technique allows the scientists to do is to actually measure mass directly at whatever scale they like, and that’s a big step forward.
INTERNATIONAL CRIMINAL COURT (ICC)
Context: India abstained from voting on a UN Human Rights Council draft resolution, in March this year, on the “situation of human rights in Myanmar.”
Essentials
- Co-sponsored by the European Union (EU) and Bangladesh, the resolution “expresses grave concern at continuing reports of serious human rights violations and abuses in Myanmar”, particularly in Rakhine, Kachin and Shan States, and calls for a full inquiry into these by the Council’s own mechanism and the International Criminal Court (ICC).
- Both India and Myanmar are non-signatory of the Rome Statute which is the founding treaty of the International Criminal Court.
The International Criminal Court
- The ICC is the world’s only permanent international criminal tribunal.
- It is headquartered in The Hague, Netherlands, and is charged with investigating and prosecuting crimes of genocide, crimes against humanity, aggression, and war crimes.
- The ICC has jurisdiction over the gravest instances of atrocity crimes and targets only the highest priority perpetrators of these crimes.
- The ICC prosecutes individuals, not organizations or governments.
- The ICC is not part of the United Nations.
- The Rome Statute is the founding treaty of the International Criminal Court.
- The UN Security Council is empowered, under the Rome Statute, to refer complaints against non-member nations to the International Criminal Court.
- Burundi is the first member-country to leave the ICC because, in September 2017, a UN commission investigating violence for over two years under President Pierre Nkurunziza recommended a criminal investigation by the court.
Terms in news
What is ‘voter apathy’?
- Voter apathy is perceived apathy among those eligible to vote in an election.
- This can happen when voters are disillusioned with the electoral process or with the political parties and candidates, or when don’t think their vote will count, or when they don’t care much for the issues around them.
- In India, voter turnouts have been going up in the past decade largely due to the Election Commission’s efforts to enhance voter participation in the country.
Paddy residue
- Farmers in Punjab use wheat residue as fodder for cattle and it’s only the stalk that is set on fire.
- The paddy residue is not used as fodder as it’s unfit and hence farmers burn both the paddy stalk and straw close to autumn every year which is a key contributing factor of pollution causing breathing problems in the northern region.





