Source: The Hindu, Live Mint and Indian Express
DROUGHT DECLARATION IN INDIA
Context: With water storage in dams dropping to a “critical” level, the Centre has issued a “drought advisory” to Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Tamil Nadu, asking them to use water judiciously.
Essentials
- The drought advisory is issued to States when the water level in reservoirs is 20% less than the average of live water storage figures of the past 10 years.
- Water falls under the State list and the advisory recommends States to use water for drinking purpose only till the dams are replenished.
- The CWC monitors water storage available in 91 major reservoirs across the country.
Drought declaration in India
- Drought is the consequence of a natural reduction in the amount of precipitation over an extended period of time leading to water shortage causing adverse impacts on vegetation, animals, and people.
Drought declaration in India – New Terminology
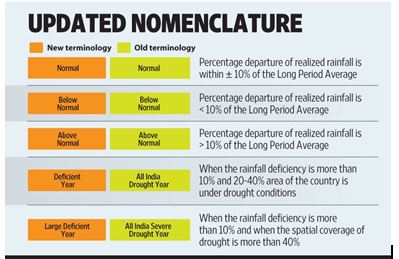
- Recently, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) officially expunged the word “drought” from its vocabulary.
- If India’s monsoon rainfall were to dip below 10 per cent of the normal and span between 20 and 40 per cent of the country’s area, it would be called a “deficient” year instead of an “All India Drought Year.”
- A more severe instance, where the deficit exceeds 40 per cent and would have been called an “All India Severe Drought Year,” will now be a “Large Deficient Year”.
- The IMD had never used the term “drought” in its forecasts and had maintained that declaring droughts was the prerogative of States.
- Declaring a drought has never been the IMD’s mandate and, in fact, not even that of the Central government, that’s because drought is not a measure of productivity (agricultural).
- Context: According to the urban air quality database for 2016 released by the WHO, of the 20 most polluted cities in the world, the top 14 are in India.
- These include Kanpur, Faridabad*, Varanasi, Gaya, Patna, Delhi, Lucknow, Agra, Muzaffarpur, Srinagar, Gurgaon*, Jaipur, Patiala, and Jodhpur—in that order.
- Varanasi is one of the cities that is part of the National Clean Air Programme, an initiative by the Union Environment Ministry to improve air quality in 100 cities by 20% at least by 2024. One of the commitments under this is to improve air quality monitoring.
*These cities are not even covered under the National Clean Air Programme.
Difference between National Clean Air Programme, National Air Quality Index and Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP):
National Clean Air Programme
- It has been launched by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
- It is a medium term(five-year action plan with 2019 as the first year) national level strategy to tackle the increasing air pollution problem across the country.
- It aims to reduce particulate matter (PM) pollution by 20-30% in at least 102 cities by 2024.
- It includes both monitoring network across the country besides ensuring comprehensive management plan for prevention, control and abatement of air pollution.
Integral components of the strategy framework:
- increasing number of existing manual and continuous monitoring stations,
- introducing rural monitoring stations
- identifying alternative technology for real-time monitoring network
- augmenting capabilities of existing monitoring stations to measure PM2.5 concentration
- an Air Information Centre as well as an Air Quality Forecasting system
- both city-specific source apportionment studies as well as a national-level emission inventory.
- While the document mentions emission reduction targets, nowhere does it actually quantify these targets.
National Air Quality Index (AQI)
- Launched by the Environment Minister, AQI is a huge initiative under ‘Swachh Bharat’.
- It is to act as ‘One Number- One Colour-One Description’ to judge the Air Quality for Common Man.
- There are six AQI categories, namely Good, Satisfactory, Moderately polluted, Poor, Very Poor, and Severe.
- It considers eight pollutants [PM10, PM5, Nitrogen dioxide (NO2), Sulphur dioxide (SO2), Carbon monoxide (CO), Ozone (O3), Ammonia (NH3) and Lead (Pb)] for which short-term (up to 24-hourly averaging period) National Ambient Air Quality Standards are prescribed.
- Associated likely health impacts for different AQI categories and pollutants have been also been suggested.
Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP)
- Executed nation-wide by Central Pollution Control Board.
- Four air pollutants are being monitored
- Sulphur Dioxide (SO2)
- Oxides of Nitrogen as NO2
- Respirable Suspended Particulate Matter (RSPM / PM10)
- Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5)
- The monitoring is being carried out with the help of:
- Central Pollution Control Board;
- State Pollution Control Boards;
- Pollution Control Committees;
- National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI), Nagpur.
‘Clean Air India Initiative’
- India in collaboration with the Netherlands has launched the ‘Clean Air India Initiative’ which aims to curb air pollution in Indian cities by promoting partnerships between Indian start-ups and Dutch companies and build a network of entrepreneurs working on business solutions for cleaner air.
Clean Sea Programme
- ‘Clean Sea Programme’ is a Sweden-led initiative to reduce littering of marine ecosystems.
New system to measure air quality
- India is tying up with the United States and Finland to develop a pollution-forecast system.
- It will help anticipate particulate matter (PM) levels at least two days in advance and at a greater resolution than what is possible now.
- At present, the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune, serves as the apex forecaster of pollution trends in Delhi, Mumbai, Pune and Ahmedabad.
- It generates a likely air quality profile, a day in advance, for these cities.
- IITM is an organisation under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES).
NAVY BOOSTS ITS AIR WARFARE CAPABILITY
Context: The Navy crossed a milestone in enhancing its anti air warfare capability, with the maiden “cooperative engagement firing” of the medium-range surface-to air missiles.
Essentials
- This was achieved by network-centric operations that helped to combine the capabilities of all military platforms in a formation.
- The firing was undertaken on the western seaboard by the INS Kochi and the INS Chennai, wherein the missiles of both ships were controlled by one ship to intercept different aerial targets at extended ranges.
US-TALIBAN TALKS FOR PEACE IN AFGHANISTAN: WHAT WE KNOW SO FAR?
Context: Officials from the United States and Taliban representatives have held six rounds of direct talks since October in Qatar’s capital Doha in a bid to end the 18-year war in Afghanistan.
Essentials
- The talks hope to preserve the post-2001 progress made in the country after the Taliban government was overthrown by a US-led military coalition for sheltering al-Qaeda, the group blamed for the 9/11 attacks.
- The Afghan government, however, is not involved in the talks as the armed group has refused to negotiate with it, deeming it illegitimate and a “puppet” of the US. The group says any engagement with the government would grant it legitimacy.
- The Taliban has long demanded the withdrawal of US troops from Afghanistan, which has been a sticking point in the meetings between the US and the group in Doha and has blocked progress in the talks.
What is the Afghan president’s loya jirga?
- Last month, the Afghan president held a loya jirga, a grand assembly which brought together more than 3,200 participants, including politicians, tribal elders and other prominent figures from across the country.
- The council, which sought to hammer out a shared strategy for future negotiations with Taliban, ended with delegates demanding an “immediate and permanent” ceasefire.
- The meeting, traditionally convened under extraordinary circumstances, was held in a bid to build consensus among various ethnic groups and tribal factions over restoring peace in Afghanistan.
ANTI-DUMPING DUTY
Context: India has begun a probe into the alleged dumping of digital printing plates from China, Japan, Korea, Taiwan and Vietnam on a complaint by a domestic manufacturer, a Commerce Ministry notification said.
Essentials
- Binding tariffs, and applying them equally to all trading partners (most-favoured-nation treatment, or MFN) are key to the smooth flow of trade in goods.
- The WTO agreements uphold the principles, but they also allow exceptions — in some circumstances.
- Three of these issues are:
- actions taken against dumping (selling at an unfairly low price);
- subsidies and special “countervailing” duties to offset the subsidies;
- emergency measures to limit imports temporarily, designed to “safeguard” domestic industries.
Countervailing duty (CVD)
- It is an additional import duty imposed on imported products (by the importing country) when such products enjoy benefits like export subsidies and tax concessions in the country of their origin.
- The objective of CVD is to nullify or eliminate the price advantage (low price) enjoyed by an imported product when it is given subsidies or exempted from domestic taxes in the country where they are manufactures.
- The WTO permits member countries to impose countervailing duty when the exporting country gives export subsidy.
Anti-Dumping Duty
- Dumping is a process where a company exports a product at a price lower than the price it normally charges on its own home market.
- An anti-dumping duty is a protectionist tariffthat a domestic government imposes on foreign imports that it believes are priced below fair market value.
- Typically anti-dumping action means charging extra import duty on the particular product from the particular exporting country in order to bring its price closer to the “normal value” or to remove the injury to domestic industry in the importing country.
- Anti-dumping duty is imposed on the basis of margin of dumping which can vary across countries, producers or exporters. Accordingly, there are variable rates of anti-dumping duty on different exporting countries, producers or exporters.
- the WTO agreement allows governments to act against dumping where there is genuine (“material”) injury to the competing domestic industry. In order to do that the government has to be able to show that dumping is taking place, calculate the extent of dumping (how much lower the export price is compared to the exporter’s home market price), and show that the dumping is causing injury or threatening to do so.
- The use of anti-dumping measure as an instrument of fair competition is permitted by the WTO.
- Disputes in the anti-dumping area are subject to binding dispute settlement before the Dispute Settlement Body of the WTO.
Anti Dumping and The Customs Duty
- Although anti-dumping duty is levied and collected by the Customs Authorities, it is entirely different from the Customs duties not only in concept and substance, but also in purpose and operation.
- The following are the main differences between the two:-
- Anti-dumping and the like measures in their essence are linked to the notion of fair trade. The object of these duties is to guard against the situation arising out of unfair trade practices while customs duties are there as a means of raising revenue and for overall development of the economy.
- Customs duties fall in the realm of trade and fiscal policies of the Government while anti-dumping and anti subsidy measures are there as trade remedial measures.
- Anti dumping duties are not necessarily in the nature of a tax measure inasmuch as the Authority is empowered to suspend these duties in case of an exporter offering a price undertaking. Thus, such measures are not always in the form of duties/tax.
- Anti dumping and anti subsidy duties are levied against exporter/country in as much as they are country specific and exporter specific as against the customs duties which are general and universally applicable to all imports irrespective of the country of origin and the exporter.
Extent of anti-dumping duty
- Under the WTO arrangement, the National Authorities can impose duties up to the margin of dumping i.e. the difference between the normal value and the export price.
- The Indian law also provides that the anti-dumping duty to be recommended/levied shall not exceed the dumping margin.
- The anti-dumping duty cannot be levied retrospectively beyond 90days from the date of issue of Notification imposing duty.
Authority For Anti Dumping
- Anti-dumping and anti subsidies & countervailing measures in India are administered by the Directorate General of anti-dumping and Allied Duties (DGAD) functioning in the Dept. of Commerce in the Ministry of Commerce and Industry and the same is headed by the “Designated Authority”.
- The Designated Authority’s function, however, is only to conduct the anti-dumping/anti-subsidy & countervailing duty investigation and make recommendation to the Government for imposition of anti-dumping or anti subsidy measures.
- Such duty is finally imposed/levied by a Notification of the Ministry of Finance.
- Thus, while the Designated Authority (in the Department of Commerce) recommends the anti-dumping duty, provisional or final , it is the Ministry of Finance, Dept. of Revenue which acts upon such recommendation within three months and imposes/levies such duty.
- Safeguard measures, on the other hand, are administered by another Authority namely, Director General (Safeguard), which functions under the Dept. of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- The Standing Board of Safeguards (chaired by the Commerce Secretary) considers the recommendations of the DG (Safeguards) and then recommends the impositions of the Safeguard Duty as it deems fit, to the Ministry of Finance which levies the duty.
Minimum Level Of Imports
Individual exporter:
- Any exporter whose margin of dumping is less than 2% of the export price shall be excluded from the purview of anti-dumping duties even if the existence of dumping, injury as well as the causal link is established.
Country:
- Further, investigation against any country is required to be terminated if the volume of the dumped imports, actual or potential, from a particular country accounts for less than 3% of the total imports of the like product.
- However, in such a case, the cumulative imports of the like product from all these countries who individually account for less than 3%, should not exceed 7% of the import of the like product.
APPEAL
- The law provides that an order of determination of existence degree and effect of dumping is appealable before the Customs, Excise and Gold (Control) Appellate Tribunal (CEGAT).
- However, as per the judicial view, only the final findings/order of the Designated Authority/Ministry of Finance can be appealed against before the CEGAT.
- Appeal cannot lie against the Preliminary findings of the Authority and the provisional duty imposed on the basis thereof.
- The Appeal to the CEGAT should be filed within 90 days.
STARLINK PROJECT
Context: SpaceX postponed the planned deployment of 60 Starlink satellites due to strong upper-altitude winds.
Essentials
- Starlink is a satellite based broadband network, with the objective of eventually building a low-cost, satellite based broadband network capable of delivering internet access to the entire globe.
- While satellite internet has been around for ages, it has generally suffered from high latency, unreliable connections, and spotty service areas.
- With Starlink, SpaceX intends to put a “constellation” of satellites in low earth orbit, thereby providing high-speed, cable-like internet to every corner of the planet.
- SpaceX will need to launch 4,425 satellites into orbit to achieve its desired coverage.
- In February 2018, SpaceX and Starlink took a huge step: The project successfully launched the first two Starlink test satellites (named Tintin A and Tintin B).
Other Competitors
- Google may be messing around with balloons (Project Loon), but Facebook is developing a satellite in house named “Athena” specifically to offer internet service to underdeveloped areas.
SpaceX
- SpaceX designs, manufactures and launches advanced rockets and spacecraft.
- The company was founded in 2002 to revolutionize space technology, with the ultimate goal of enabling people to live on other planets.
- SpaceX has gained worldwide attention for a series of historic milestones.
- It is the only private company capable of returning a spacecraft from low Earth orbit, which it first accomplished in 2010.
- The company made history again in 2012 when its Dragon spacecraft became the first commercial spacecraft to deliver cargo to and from the International Space Station.
- SpaceX successfully achieved the historic first reflight of an orbital class rocket in 2017, and the company now regularly launches flight-proven rockets.
- In 2018, SpaceX began launching the world’s most powerful operational rocket by a factor of two.
- Building on the achievements of Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy, SpaceX is working on a next generation of fully reusable launch vehicles that will be the most powerful ever built, capable of carrying humans to Mars and other destinations in the solar system.
Terms in news
European Alliance of People and Nations
- Italy’s Deputy Prime Minister and figurehead for the far right in Europe, Matteo Salvini, launched the campaign for the European Alliance of People and Nations, alongside allies from Germany to Denmark, on a platform invoking tougher immigration rules and in some cases Euroscepticism.
- Euroscepticism, also known as EU-scepticism, means criticism of the European Union (EU) and European integration.
Indo-Pacific Vision
- The Indo-Pacific wing has been set up in the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) in April 2019.
- The renaming of the U.S. Pacific Command to U.S. Indo-Pacific Command as well as the Asia Reassurance Initiative Act in December 2018 showcase Washington’s more serious engagement with the Indo-Pacific.
- The Free and Open Indo-Pacific concept was unveiled by Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe in 2016.
Major irritants in the Indo-U.S. trade relations
- Disagreements over ICT, dairy products, medical devices, India’s e-commerce policy and the U.S.’s H-1B visa policies are yet to be resolved.
- Trump’s March announcement that preferential trade benefits for India under the U.S.’s GSP program will be withdrawn and the U.S. requiring India to stop its imports of Iranian oil from May, have added to the strain on the relationship.
Taiwan
- Taiwan’s legislature voted to legalize same-sex marriage, in a first in Asia and a boost for LGBT rights activists who had championed the cause for two decades.





