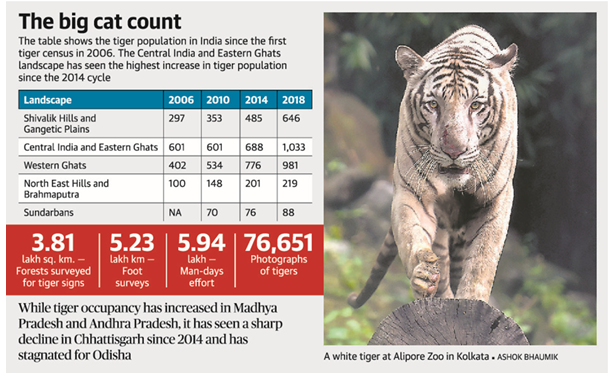
India has nearly 3,000 tigers
Ecology
- India has 2,967 tigers, a third more than in 2014.
- Madhya Pradesh saw the highest number at 526, closely followed by Karnataka (524) and Uttarakhand (442).
- Chhattisgarh and Mizoram saw a decline in tiger population and all other States saw an increase.
- The survey, the fourth such since 2006, is conducted once in four years.
- While the Pench Tiger Reserve in Madhya Pradesh recorded the highest number of tigers, the Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve in Tamil Nadu registered the “maximum improvement” since 2014.

Pench, Periyar rated top tiger reserves
Ecology
- Madhya Pradesh’s Pench sanctuary and Kerala’s Periyar sanctuary emerged as the best managed tiger reserves in the country, according to an evaluation of India’s 50 tiger sanctuaries released along with the 4th National Tiger Estimation (Tiger census).
- The Dampa and Rajaji reserves, in Mizoram and Uttarakhand respectively, were left at the bottom of the ladder with a score of 42.97% and 44.53% respectively. The top performers scored 93.75%. A score of 41% and above was marked as ‘fair’ and those 75% and above rated ‘very good.’
- The sanctuaries, which spanned 80 States, were divided into five geographic clusters. On the whole, the Western Ghats cluster comprising reserves in Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka scored an average of 81%.
- Kerala had the best kept reserves followed by Madhya Pradesh. Chhattisgarh was the ‘least performing State’ in reserve management.
Government’s plan to develop 17 ‘iconic tourist sites’
Infrastructure

- In July 2018, govt had said 17 ‘iconic tourist sites’ would be developed.
- These were Taj Mahal and Fatehpur Sikri in Uttar Pradesh, Ajanta and Ellora caves in Maharashtra, Humayun’s Tomb, Red Fort and Qutub Minar in Delhi, Colva Beach in Goa, Amer Fort in Rajasthan, Somnath and Dholavira in Gujarat, Khajuraho in Madhya Pradesh, Hampi in Karnataka, Mahabalipuram in Tamil Nadu, Kaziranga in Assam, Kumarakom in Kerala and Mahabodhi in Bihar.
- However, now these sites could see some changes, with govt ordering a review of the sites included in the project.
Odisha is origin of Rasagola
Art & Culture

- The rasagola, a popular dessert of Odisha, has received the Geographical Indication tag from the Registrar of Geographical Indication after years of controversy around the sweet.
- ‘Odisha Rasagola’ is a sweet from the state of Odisha made of chhena (cottage cheese) cooked in sugar syrup, which is very soft to feel, is juicy and non- chewy in consistency and can be swallowed without teeth pressure.
- Colour development of the ‘Odisha Rasagola’ is very specific, where without addition of external colour, various intensely-coloured rasagolas are prepared using the principle of caramelisation of sugar with specific methods of preparation.
- Both Odisha and West Bengal have been contesting the origin of the rasagola.
- Historical records submitted say the ‘Odisha Rasagola’ has an age-old tradition and is associated with world famous Puri Jagannath Temple.
Dam Safety Bill
Environment

- Opposition expressed deep reservation about the Centre’s decision to introduce the Dam Safety Bill, 2019, saying that the legislation, which is ostensibly aimed at providing uniform safety measures across the country, will undermine the powers of the State governments since water is a State subject.
- However, the govt argued that the Centre was empowered to enact a law on the subject, especially as 92% of the dams involved two or more States, and Article 246 and 56 empowered the Centre to intervene.
Indemnity to successful bidders under IBC
Economy

- Extending indemnity to successful bidders of companies that have defaulted on loans, govt said it would not initiate any criminal proceedings against those who buy out a bankrupt company and no tax claim would be raised against them after implementation of a resolution plan.
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Amendment) Bill, 2019 makes it “binding on the government” that it will “not raise any further claim after resolution plan is approved,”.
- Under the IBC, loan defaulting companies are auctioned and the successful bidder, called resolution applicant, takes over such firms after paying an amount they had bid for.
- However, govt said criminal matters would continue to be pursued against individuals of the loan-defaulting companies.
DIIs raise stake in listed firms
Economy

- Domestic institutional investors (DIIs) are steadily increasing their stake in listed entities even as foreign portfolio investors (FPIs) continue to be the largest category of non-promoter shareholders in the Indian capital market.
- Holding of DIIs include mutual funds, insurance companies, banks, financial institutions and pension funds.
- However, the holding of mutual funds and DIIs, as a whole, is still lower than the overall FPI ownership.
- The widest gap between FPI and DII holding was seen in the quarter ended March 31, 2015, when DII holding was almost half that of their foreign counterparts.
- Over a 10-year period from June 2009, however, while FPI ownership has risen from 13.6% to 19.8%, DII ownership has gone up only marginally, from 11.66% to 13.78%.
End-use norms for external commercial borrowings eased
Economy

- The RBI has decided to relax norms for end-use of funds raised via the external commercial borrowing (ECB) route by companies and non-banking finance companies.
- The relaxation was for working capital requirements, general corporate purposes and repayment of rupee loans.
- Eligible borrowers will now be allowed to raise ECBs with a minimum average maturity period of 10 years for working capital purposes and general corporate purposes.





