Source: The Hindu, Live Mint and Indian Express
SPECIAL CATEGORY STATUS
Context: Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister met Prime Minister to raise the unfulfilled demand of the Special Category Status (SCS).
Essentials
What is Special Category Status?
- In 1969, the Fifth Finance Commission proposed Special Category States based on recommendations made by the National Development Council.
- The idea was to give preferential treatment to certain states that were deemed historically disadvantaged, by allocating more central funds and tax concessions.
- The Constitution does not have any provision for categorisation of any State as a Special Category Status (SCS) State.
- In the past, the NDC considered factors such as
- difficult and hilly terrain;
- low population density and/or a sizeable share of tribal population;
- strategic location along borders;
- economic and infrastructural backwardness, and;
- non-viable nature of state finances.
What assistance do states with Special Category Status get?
- Preferential treatment in getting central funds assistance
- Concessions in income-tax rates, excise and customs duties to attract industries to the state
- SCS states would get 30% of the normal central assistance (30% of centre’s gross budget to these states); with the remaining 70% being split among other states based on their population, per capita income, and fiscal performance.
- These states can avail the benefit of debt swapping and debt relief schemes
- In the case of centrally sponsored schemes and external aid, special category states get it in the ratio of 90 per cent grants and 10 per cent loans, while other states get 30 per cent of their funds as grants.
- Tax breaks to attract investment
14th Finance Commission and the SCS states
- The 14th Finance Commission did away with distinction between general and special category states since it had taken into account the level of backwardness of states in the proposed transfer of funds to states.
- The idea was that adequate resources would be allocated through tax devolution and grants to address interstate inequalities.
- The special category status was therefore restricted to the three hill states ( J&K, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand) and those in the Northeast by the 14th Finance Commission.
- It was also decided that a revenue deficit grant would be provided for certain states for which devolution alone would be insufficient.
- Andhra was one of the states that were to be given a revenue deficit grant.
Why does Andhra Pradesh wants to get Special Category Status?
- When Andhra Pradesh was bifurcated in 2014, it sought Special Category Status on the grounds that it was at a disadvantage, since it would lose a significant amount of revenue as a result of Hyderabad going to Telangana, the new state that came into existence in June 2014.
SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT RULES, 2016
Context: More than six years after a fire at the Bandhwari landfill site off the Gurugram-Faridabad road led to the shutting down of the treatment plant here, the Municipal Corporation of Gurugram has failed to find a tangible solution to solid municipal waste management in the Millennium City.
Essentials
Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016
- These rules are the sixth category of waste management rules brought out by the ministry, as it has earlier notified plastic, e-waste, biomedical, hazardous and construction and demolition waste management rules.
Salient Features
- These Rules are now applicable beyond municipal areas and will extend to urban agglomerations, census towns, notified industrial townships, areas under the control of Indian Railways, airports, airbase, port and harbour, defence establishments, special economic zones, State and Central government organizations, places of pilgrims, religious & historical importance.
- The responsibility of generators has been introduced to segregate waste into three categories – Wet (biodegradable), Dry (non-biodegradable) and Domestic Hazardous waste (diapers, napkins, mosquito repellents, cleaning agents etc.).
- The source segregation of waste has been mandated to channelize the waste to wealth by recovery, reuse and recycle.
- The generator will have to pay ‘User Fee’ to the waste collector and a ‘Spot Fine’ for littering and non-segregation, the quantum of which will be decided by the local bodies.
- Waste processing facilities will have to be set up by all local bodies having 1 million or more population within two years.
- Integration of waste pickers/ragpickers and waste dealers/Kabadiwalas in the formal system.
- New townships and Group Housing Societies have been made responsible to develop in-house waste handling, and processing arrangements for bio-degradable waste.
- Every street vendor should keep suitable containers for storage of waste generated during the course of his activity.
- The developers of Special Economic Zone, industrial estate, industrial park to earmark at least 5% of the total area of the plot or minimum 5 plots/sheds for recovery and recycling facility.
- Construction of landfill on the hills shall be avoided.
- All manufacturers of disposable products such as tin, glass, plastics packaging etc. or brand owners who introduce such products in the market shall provide necessary financial assistance to local authorities for the establishment of waste management system.
- Collect Back scheme for packaging waste: All such brand owners who sale or market their products in such packaging material which are non-biodegradable should put in place a system to collect back the packaging waste generated due to their production.
- All industrial units using fuel and located within 100 km from a solid waste based Refuse-derived fuel (RDF) plant shall make arrangements within six months from the date of notification of these rules to replace at least 5 % of their fuel requirement by RDF so produced.
- Non-recyclable waste having calorific value of 1500 K/cal/kg or more shall not be disposed of on landfills and shall only be utilized for generating energy.
- Collection and disposal of sanitary waste: The manufacturers or brand owners of sanitary napkins are responsible for awareness for proper disposal of such waste by the generator and shall provide a pouch or wrapper for disposal of each napkin or diapers along with the packet of their sanitary products.
- The rules have mandated bio‐remediation or capping of old and abandoned dump sites within five years.
- The Department of Fertilisers, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers should provide market development assistance on city compost and ensure promotion of co‐marketing of compost with chemical fertilisers.
- The Ministry of Agriculture should provide flexibility in Fertiliser Control Order for manufacturing and sale of compost.
Revision of parameters and existing standards
- The landfill site shall be:
- 100 metres away from a river,
- 200 metres from a pond,
- 500 metres away from highways, habitations, public parks and water supply wells and
- 20 km away from airports/airbase.
- Emission standards are completely amended and include parameters for dioxins, furans, reduced limits for particulate matters from 150 to 100 and now 50.
Do you know?
- Solid waste generated in India in decreasing order: e-waste > hazardous waste > plastic waste > biomedical waste.
NOTA
Context: NOTA – slight hike in satellite constituencies.
Essentials
- If the right to vote is a statutory right, then the right to reject a candidate is a fundamental right of speech and expression under the Constitution.
- The system of negative voting exists in several other countries.
- Even in Parliament, the MPs have the option to abstain during a vote.

What is NOTA?
- This was introduced to give voters a right to reject the candidates put up by the political parties.
- Electronic voting machines (EVM) in India have the ‘None Of The Above‘ (NOTA) button at the bottom of the list of candidates.
- None of the Above (NOTA) option also has a symbol to facilitate the voter to exercise the NOTA option.
- A candidate belonging to a particular political party fights on the party’s symbol.
- An independent candidate fights on the symbol allotted to him by the Election Commission of India.
- The NOTA option is meant only for universal adult suffrage and direct elections.
- The option is available to the public only during Lok Sabha, state assembly and Panchayat and Municipal body elections.
- Implementing the Supreme Court order, the Election Commission of India (ECI) withdrew the provision of None Of The Above (NOTA) from elections to Rajya Sabha and legislative council in states.
How is a NOTA vote cast?
- The EVMs have the NOTA option at the end of the candidates’ list.
- Earlier, in order to cast a negative ballot, a voter had to inform the presiding officer at the polling booth.
- A NOTA vote doesn’t require the involvement of the presiding officer.
When was NOTA first used in India?
- The EC, on the directions of the SC, introduced the NOTA option for the first time in the 2013 Assembly elections of Chhattisgarh, Mizoram, Rajasthan, Delhi and Madhya Pradesh.
- In 2014, the EC introduced the option in the Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha elections.
There was a similar provision before NOTA. What was it?
- The voters had the right of choosing none of the contesting candidates earlier as well. But before introduction of NOTA, a voter had to inform the polling officer of her decision, as per Rule 49 O of the Representation of People’s Act. The polling officer would then record her vote in Form 17 and take the signature or thumb impression of the voter.
- This provision went against the basic principle of secret voting as practiced in India, according to Section 128 of the Representation of People’s Act. The voter’s choice of not voting for any of the candidates could not be kept secret as the ballot paper bearing her name and signature would be enumerated along with counting of other votes. NOTA restored secret ballot in election.
How are 49(O) and NOTA different?
- The Section 49 (O) stood annulled after the SC cleared the NOTA provision.
- It gave the poll officials a chance to find out the reason behind the rejection of a candidate through the voter’s remarks in Form 17A.
- Through NOTA, the officials cannot find out the reason for the rejection.
- Moreover, it protects the identity of a voter, thus keeping the concept of secret balloting intact.
What difference does NOTA make?
- The NOTA option cannot impact the results of the elections.
- The NOTA option on EVMs has no electoral value.
- Even if the maximum number of votes cast is for NOTA, the candidate getting the most of the remaining votes would be declared winner.
- NOTA votes are treated as invalid or no votes.
- It is not a negative vote, but a neutral one that records a voter’s rejection of candidates.
- In the recent past, State Election Commissions in Maharashtra and Haryana ruled that fresh polls would be held if more votes were cast for NOTA. But this was restricted to municipal and panchayat elections and it’s not clear if this would stand up to legal scrutiny.
Red Alert Constituencies
- These are those which have 3 or more candidates with criminal cases contesting elections.
DR LEE JONG WOOK MEMORIAL PRIZE FOR PUBLIC HEALTH
Context: Professor Dr Balram Bhargava, a renowned cardiologist is the winner of the 2019 Dr Lee Jong wook Memorial Prize for Public Health for his achievements as a clinician, innovator, researcher and trainer.
Dr Balram Bhargava is the Director General, Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)
Essentials
- The Dr LEE Jong-wook Memorial Prize for Public Health was established in 2008, and is awarded to individuals, institutions, and governmental or non-governmental organizations who have made an outstanding contribution to public health.
- The Prize aims at rewarding work that has extended far beyond the call of normal duties, and it is not intended as a reward for excellent performance of duties normally expected of an official position of a governmental or intergovernmental institution.
- The prize is awarded once a year, and is presented at a special ceremony during the World Health Assembly.
Procedure for the proposal and selection of candidates
- Any national health administration of a Member State of the World Health Organization, or any former recipient of the Prize, may put forward the name of a candidate for the Prize.
- The Prize Selection Panel recommends candidates to the Executive Board, which designates the recipient (or recipients) of the Prize.
NATIONAL DISASTER RESPONSE FORCE (NDRF)
Context: Heavy rain that led to flash floods left hundreds of houses submerged in Tripura and the National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) is working hard to evacuate members of these families with their belongings to safer places.
Essentials
National Disaster Response Force (NDRF)
- It was constituted in 2006 under the Disaster Management Act for the purpose of specialized response to natural and man-made disasters.
- At present, National Disaster Response Force consist of 12 battalions, three each from the BSF and CRPF and two each from CISF, ITBP and SSB.
- All the 12 battalions have been equipped and trained to respond natural as well as man-made disasters.
- Battalions are also trained and equipped for response during chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear (CBRN) emergencies.
- In the beginning, the personnel of NDRF were deployed for routine law and order duties also but in 2007 it has been made a dedicated force for disaster response related duties.
- The first major test of disaster for NDRF was Kosi Floods in 2008.
- It functions under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
LOCATIONS OF NDRF BNs
- These NDRF battalions are located at 12 different locations in the country based on the vulnerability profile of country and to cut down the response time for their deployment at disaster site.
- Guwahati
- Haringhata
- Mundali
- Arakkonam
- Pune
- Vadodara
- Bhathinda
- Ghaziabaad
- Patna
- Vijayawada
- Varanasi
- Doimukh
Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar
- The award is to be announced every year on 23rdJanuary on the birth anniversary of Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose.
- All Indian Citizens and organizations, who have excelled in areas of Disaster Management, are eligible for the
- For the year 2019, 8th Battalion of National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) located at Ghaziabad has been selected for the Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar for its commendable work in Disaster Management.
WHAT IS BRAIN FINGERPRINTING?
- Brain fingerprinting is a computer based technology designed to find out if the individual is telling the truth by measuring electrical brain wave responses to words, phrases, or pictures presented on a computer screen.
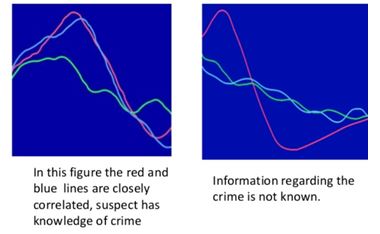
How Brain Waves are used to detect guilt?
- A suspect is tested by looking at three kinds of information represented by different coloured lines.
- RED: Information the suspect is expected to know. It arises due to target type stimulus.
- GREEN: Information not to suspect. The irrelevant stimuli is responsible for this type of brain waves.
- BLUE: Information of the crime that only perpetrator would know. This occurs due to probes.
- If the red and blue lines are closely correlated, suspect is considered to have the knowledge of the crime.
NATIONAL OFFSHORE WIND ENERGY POLICY 2015
Context: Since 2014, India added 28,000 MW of solar power and 14,500 MW of wind power.
- Today, India has 30,600 MW of solar power capacity and 35,600 MW of wind power.
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has declared medium- and long-term targets for offshore wind power capacity addition.
- The target is 5 GW by 2022 and 30 GW by 2030.
- In April 2018, a call for expression of interest to set up 1 GW of offshore wind farm in Gulf of Khambhat region off Gujarat coast was also floated.
Essentials
National Offshore Wind Energy Policy 2015
- In September 2015, the Union Cabinet has approved the National Offshore Wind Energy Policy 2015.
- Since India has around 7600 Kilometres of coast, the prospects of development of offshore wind power are very bright.
- Worldwide, offshore wind power projects totalling 7.5 GW capacity have been installed.
- Globally, UK tops the list of offshore wind markets, followed by Germany, Taiwan, China and the USA.
The offshore wind faming is attractive because of several reasons such as:
- stronger winds for efficient generation of power;
- no impact on real estate value of land as in case of onshore wind farming;
- its ability to fulfil the demand of the heavily populated coastal regions;
- no significant environment costs.
- Government has paved the way for development of the offshore wind farms up to the seaward distance of 200 Nautical Miles (within its Exclusive Economic Zone) from the base line.
- The Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) has been authorized as the Nodal Ministry for use of offshore areas within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of the country (beyond the 12 nm limit and up to 200 nm).
- The National Institute of Wind Energy (NIWE) has been authorized as the Nodal Agency for development of offshore wind energy (up to 12 nautical miles (nm) from the baseline).
- In terms of wind power installed capacity India is globally placed at 4thposition after China, USA and Germany.
- India has established a strong manufacturing base of wind power equipment in the country.
- Comprehensive Guidelines for Development of On-shore Wind Power Projects in the country have been formulated and issued in October 2016.
WHAT IS THE JOIDES RESOLUTION?
Context: In a first, scientists have discovered the remnants of seawater dating back to the Ice Age, tucked inside rock formations in the middle of the Indian Ocean.
When they extracted the water, they noticed their preliminary tests were coming back salty — much saltier than normal seawater.
Essentials
- The JOIDES Resolution (JR) is a research vessel that drills into the ocean floor to collect and study core samples.
- Scientists use data from the JR to better understand climate change, geology and Earth’s history.
- It is a part of the International Ocean Discovery Program and is funded by the National Science Foundation.
- The ship, the JOIDES Resolution, is specifically built for ocean science and is equipped with a drill that can extract cores of rock over a mile long from up to three miles beneath the seafloor.
About IODP
- The International Ocean Discovery Programme (IODP) is an international marine research collaboration that explores Earth’s history and dynamics using ocean-going research platforms to recover data recorded in seafloor sediments and rocks and to monitor sub-seafloor environments.
- India’s Ministry of Earth Science (MoES) is one of the Additional Funding Partners of the Programme.
SCIENCE PLAN 2013-2023
- The science plan under IODP identifies 14 challenge questions in the four areas of climate change, deep life, planetary dynamics, and geohazards.





